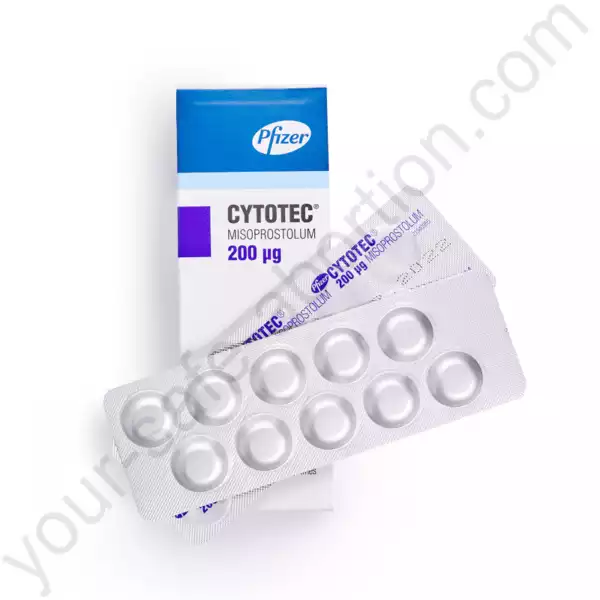
Product description
Cytotec Tabet (Misoprostol) — The Complete Product Guide
Introduction:
Cytotec, also known by its generic name Misoprostol, is a medication primarily used to prevent stomach ulcers in certain patients who take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). However, it is also used off-label for medical abortion and to induce labor.
This comprehensive product guide aims to provide you with important information about Cytotec, its uses, dosage, side effects, and precautions.
Nonetheless, consulting a healthcare professional for personalized guidance is crucial before using Cytotec or any other medication.
Our online pharmacy has other medications in stock that contain identical doses of Misoprostol: Misoprostol, Misoprost-200, Cytolog, and MisoOne.
What is Cytotec Used For?
Cytotec is primarily used in combination with mifepristone for medical abortion. It works by causing the uterus to contract and expel pregnancy tissue. Additionally, Cytotec is used to manage incomplete miscarriages and to prevent gastric ulcers in individuals taking certain medications.
- Preventing Stomach Ulcers: Cytotec is effective in preventing stomach ulcers, especially in individuals who are at risk due to long-term use of NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or aspirin. It reduces stomach acid and increases mucus production, protecting the stomach lining.
- Medical Abortion: Cytotec can be used in combination with another medication, Mifepristone, to safely and effectively induce a medical abortion for pregnancies up to 11 weeks gestation. Nonetheless, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider for guidance and supervision throughout the process.
- Labor Induction: In certain situations, such as when a pregnancy has gone beyond the due date or the mother’s health is at risk, doctors may use Cytotec to induce labor. Healthcare professionals should carefully monitor this process to ensure safety.
Can You Buy Cytotec Online?
Yes, you can buy Cytotec online through reputable healthcare providers like Panda Healthcare. Purchasing Cytotec online offers a convenient and discreet way to access the medication, ensuring you receive the care you need from the comfort of your home.
However, obtaining Cytotec from a licensed and trustworthy source is crucial to guarantee its safety and authenticity.
How to Safely Buy Cytotec Online
- Consultation: Before you buy Cytotec online, you’ll typically need to complete a medical consultation to confirm eligibility. This step ensures the medication is safe and appropriate for your situation.
- Prescription: A licensed healthcare provider will issue a prescription if Cytotec suits you.
- Delivery: Once approved, you can buy Cytotec online and deliver it directly to your doorstep in discreet packaging.
Why Choose Cytotec?
- Effectiveness: Cytotec is highly effective when used correctly for medical abortion or managing miscarriages.
- Privacy: The ability to buy Cytotec online allows you to maintain your privacy and avoid unnecessary visits to a clinic.
- Convenience: Online access to Cytotec simplifies the process, making obtaining the medication you need easier.
Dosage and Administration:
- For Medical Abortion or Miscarriage Management:
- Follow the dosage instructions provided by your healthcare provider.
- For medical abortion, Cytotec is typically taken 24–48 hours after mifepristone.
- For Ulcer Prevention:
- Take Cytotec as directed by your healthcare provider, usually in combination with NSAIDs.
- The typical dosage for ulcer prevention is 200 mcg, taken 2–4 times daily with meals and at bedtime.
Always consult with a healthcare professional to ensure proper use and address concerns.
When used for medical abortion or labor induction, the dosage and administration protocols are determined by healthcare professionals based on various factors, including gestation period and medical history.
Possible Side Effects:
While Cytotec can be an effective medication, like any drug, it may cause side effects, which can vary from person to person. Common side effects may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, flatulence, or headache. These side effects are generally mild and tend to resolve on their own.
Less common but potentially serious side effects may include allergic reactions, severe abdominal pain or cramping, heavy vaginal bleeding, or signs of infection. If you experience severe or persistent side effects, seek medical attention promptly.
Precautions and Warnings:
Cytotec should not be used if you have an allergy to Misoprostol or similar medications, are pregnant, or are experiencing complications during pregnancy. It should also be used with caution in individuals with certain medical conditions, such as kidney or liver disease or a history of asthma. Always disclose your complete medical history to your healthcare provider before using Cytotec.
Moreover, it is essential to remember that Cytotec is not designed for self-medication without medical supervision. Always consult a healthcare provider to determine if it is appropriate for your specific condition and to receive proper guidance regarding dosage, administration, and potential risks.
Self-Care During Cytotec Using
1. Educate Yourself About the Process
- Understand How Cytotec Works: Know the purpose, dosage, and expected effects of Cytotec based on your specific use (e.g., medical abortion, miscarriage management, or ulcer prevention).
- Follow Medical Guidance: Always use Cytotec under the supervision of a healthcare provider and follow their instructions carefully.
- Know What to Expect: Be aware of common side effects (e.g., cramping, bleeding, nausea) and warning signs that may require medical attention.
2. Prepare Your Environment
- Create a Comfortable Space: If using Cytotec at home (e.g., for medical abortion), choose a quiet, private, and comfortable place where you can rest.
- Gather Supplies: Have essentials ready, such as:
- Maxi pads (avoid tampons to reduce infection risk).
- Pain relievers (e.g., ibuprofen or acetaminophen, as recommended by your doctor).
- A heating pad or hot water bottle for cramping.
- Hydrating drinks (water, herbal tea) and light snacks.
- A trusted friend or partner for emotional and physical support.
3. Manage Physical Discomfort
- Pain Relief: Take over-the-counter pain relievers as your healthcare provider recommends to manage cramping.
- Heat Therapy: Use a heating pad or hot water bottle on your lower abdomen to ease cramps.
- Rest: Allow your body time to recover by resting and avoiding strenuous activities.
- Hydration and Nutrition: Drink plenty of fluids and eat light, nutritious meals to maintain energy levels.
4. Monitor Your Health
- Track Bleeding and Symptoms: Expect heavy bleeding and clotting, which are typical during a medical abortion or miscarriage. However, seek medical help if:
- Bleeding soaks through more than two maxi pads per hour for two consecutive hours.
- You experience severe pain that isn’t relieved by medication.
- You develop a fever (above 100.4 °F (ca. 38 °C)) or chills, which could indicate infection.
- Follow-Up Care: Attend any scheduled follow-up appointments to confirm the process is complete and address any concerns.
5. Prioritize Emotional Well-Being
- Acknowledge Your Feelings: It’s normal to experience a range of emotions, including relief, sadness, or guilt. Allow yourself to process these feelings without judgment.
- Seek Support: Talk to a trusted friend, family member, or counselor about your experience. Support groups or hotlines can also provide comfort and guidance.
- Practice Self-Compassion: Be kind to yourself and recognize that you made the best decision for your circumstances.
6. Prevent Infections
- Avoid Tampons: Use maxi pads instead of tampons to reduce the risk of infection.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently and keep the genital area clean.
- Avoid Sexual Activity: Refrain from intercourse for at least 1–2 weeks or as advised by your healthcare provider to prevent infection.
7. Plan for Recovery
- Take Time Off: Take a day or two off work or school to rest and recover.
- Avoid Heavy Lifting: Refrain from strenuous activities for at least a week to allow your body to heal.
- Listen to Your Body: If you feel tired or unwell, permit yourself to rest.
8. Know When to Seek Help
- Recognize Warning Signs: Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you experience:
- Excessive bleeding.
- Severe or persistent pain.
- Foul-smelling discharge.
- Signs of infection (fever, chills, or weakness).
- Emergency Care: If you cannot reach your provider, visit the nearest emergency room.
9. Use Cytotec Responsibly for Ulcer Prevention
- If using Cytotec for ulcer prevention:
- Take it exactly as prescribed by your doctor.
- Combine it with meals and at bedtime to maximize its protective effects.
- Avoid alcohol and NSAIDs (unless advised otherwise by your doctor) to reduce stomach irritation.
10. Reflect and Reconnect
- Journal Your Experience: Writing about your feelings and experiences can help you process emotions.
- Reconnect with Your Body: Engage in gentle activities like yoga, walking, or meditation to rebuild a positive connection with your body.
- Celebrate Your Strength: Recognize the courage it takes to make difficult decisions and care for yourself.
Conclusion:
Cytotec, or Misoprostol, is a medication primarily used for preventing stomach ulcers in patients who take NSAIDs. It is also used off-label for medical abortion and labor induction. While it can be beneficial in specific situations, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional before using Cytotec to ensure its safety and appropriateness for your individual needs.
This product guide aims to provide an overview of Cytotec, but it does not replace professional medical advice.
 Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Русский
Русский
Because the personnel at panda.healthcare responds so quickly; the service is amazing. Additionally; take less time to resolve issues while still assuring complete satisfaction. Shop with complete assurance.