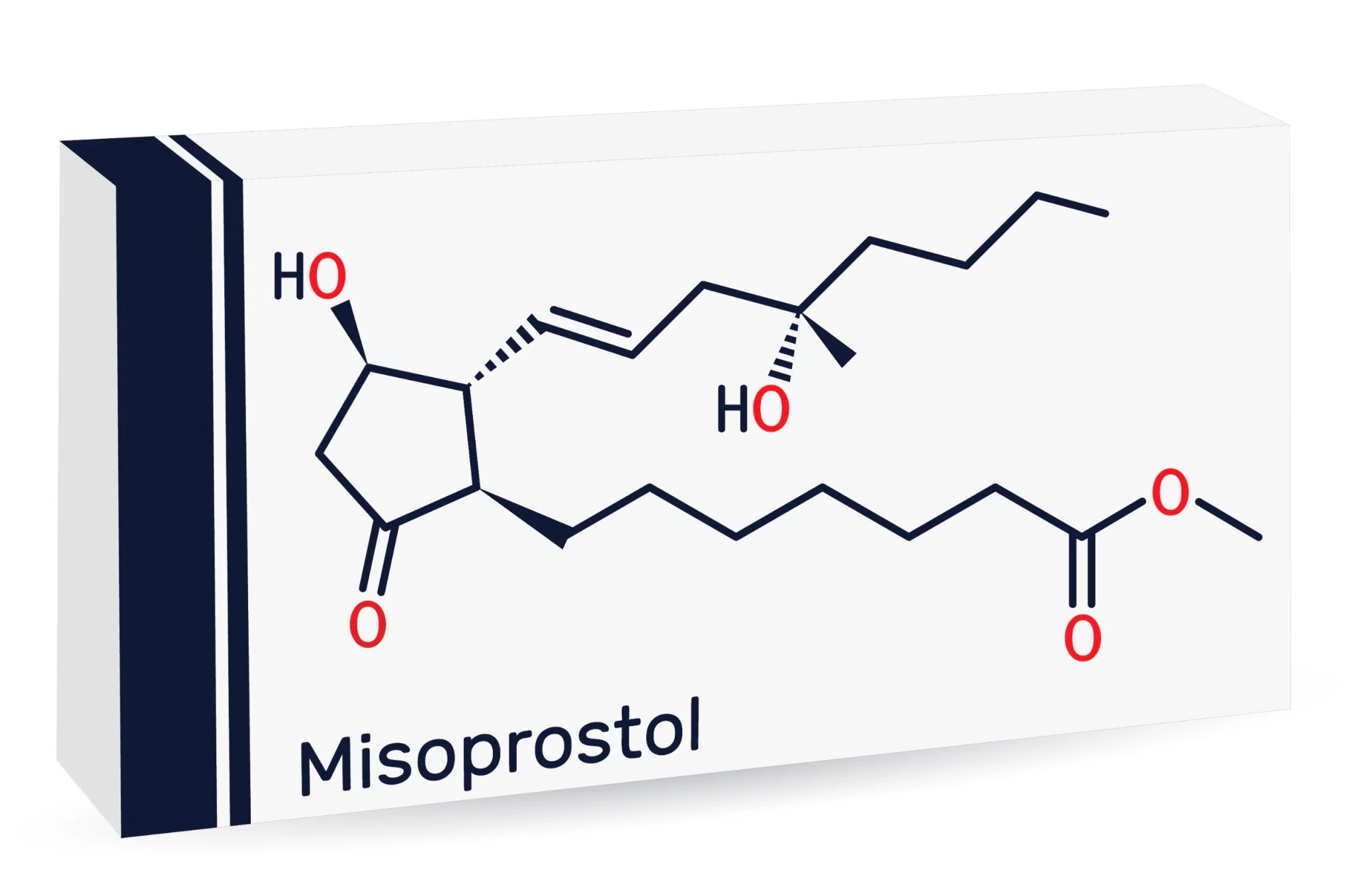
Misoprostol: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
Misoprostol, a medication with diverse applications, holds a significant place in the realm of healthcare. Its multifaceted properties make it invaluable in various medical fields, including obstetrics, gynecology, and gastroenterology. This article aims to thoroughly understand Misoprostol, delving into its mechanisms of action, medical applications, dosages, administration routes, safety considerations, and future prospects.
1. What is Misoprostol?
Overview: Misoprostol is a synthetic prostaglandin E1 analog initially developed to prevent and treat gastric ulcers. However, its versatility has led to its widespread use in other medical contexts.
Mechanism of Action: Misoprostol exerts its effects by binding to prostaglandin receptors, leading to various physiological responses such as uterine contractions, cervical ripening, gastric mucosal protection, and inhibition of gastric acid secretion.
2. Medical Applications of Misoprostol
1. Medical Abortion: Misoprostol is a crucial component in Medical Abortion regimens, where it is used to induce uterine contractions and expel the contents of the uterus, effectively terminating pregnancy. It is often administered following Mifepristone, a progesterone antagonist.
2. Induction of Labor: In obstetrics, this drug is utilized for inducing labor in pregnant individuals with indications such as post-term pregnancy, preterm premature rupture of membranes, or fetal distress. It helps stimulate uterine contractions and facilitate cervical ripening.
3. Prevention of Postpartum Hemorrhage: This medicine is employed prophylactically to prevent postpartum hemorrhage, a leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide. Promoting uterine contractions and tone reduces the risk of excessive bleeding following childbirth.
4. Treatment of Gastric Ulcers: Originally developed for this purpose, the medicine remains a valuable medication for treating gastric ulcers, particularly those induced by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). It helps protect the gastric mucosa and promote ulcer healing.
3. Dosages and Administration
Dosage Regimens: The dosage of Misoprostol varies depending on the medical indication, patient characteristics, and healthcare provider’s recommendations. Dosage forms commonly include oral tablets, vaginal inserts, or sublingual formulations.
Administration Routes: It can be administered orally, vaginally, sublingually, or rectally, depending on the medical context and individual preferences. Each route of administration has its advantages and considerations.
4. Medical Abortion: The Role of Misoprostol
Medical Abortion, also known as Medication Abortion, offers individuals a non-surgical option for terminating pregnancies safely and effectively. Central to this method is Misoprostol, a prostaglandin E1 analog that induces uterine contractions and facilitates the expulsion of the pregnancy tissue. This subsection provides a comprehensive exploration of the use of Misoprostol in Medical Abortion, including its mechanisms of action, administration protocols, effectiveness, safety considerations, and patient experiences.
4.1. Understanding Medical Abortion
Overview: Medical Abortion involves the use of medications to terminate a pregnancy, typically within the first trimester. It offers individuals a non-invasive option that can be administered in a clinical setting or at home under medical supervision.
Components of Medical Abortion: Medical Abortion protocols often include a combination of medications, with Misoprostol being one of the critical agents used alongside Mifepristone, a progesterone antagonist.
4.2. Mechanisms of Action of Misoprostol
Uterine Contractions: This substance stimulates uterine contractions by binding to prostaglandin receptors in the uterine muscle, expulsing the pregnancy tissue.
Cervical Softening: Besides promoting uterine contractions, Misoprostol also softens and dilates the cervix, facilitating the passage of the pregnancy tissue.
4.3. Administration Protocols
Timing and Dosage: Misoprostol is typically administered 24 to 48 hours after the administration of Mifepristone. The recommended dosage of Misoprostol is commonly 800 mcg administered orally or 800 to 1200 mcg administered vaginally.
Route of Administration: Misoprostol can be administered orally, buccally (placed between the cheek and gum), or vaginally. Vaginal administration is typically preferred due to higher bioavailability and faster onset of action.
4.4. Effectiveness and Success Rates
High Efficacy: Clinical studies have consistently demonstrated high efficacy rates for Medical Abortion with Misoprostol, successfully rates exceeding 95% in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Gestational Age Considerations: The effectiveness of Medical Abortion with Misoprostol may vary depending on gestational age, with higher success rates observed in earlier gestational ages.
4.5. Safety Considerations and Potential Side Effects
Common Side Effects: Common side effects of Misoprostol in Medical Abortion may include abdominal cramping, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, and chills. These side effects are usually transient and resolve with time.
Serious Complications: While rare, serious complications such as excessive bleeding, incomplete abortion, or uterine infection may occur and require medical attention.
4.6. Patient Experience and Support
Counseling and Support: Individuals undergoing Medical Abortion with Misoprostol should receive comprehensive counseling and support from healthcare providers, including information about the procedure, potential side effects, and available resources for assistance.
Follow-Up Care: Follow-up appointments are essential to ensure the completion of the abortion process, assess for any complications, and provide additional support as needed.
4.7. Conclusion
Empowering Reproductive Choice: The use of Misoprostol in Medical Abortion offers individuals a safe and effective option for terminating pregnancies on their terms, without the need for invasive surgical procedures.
Ensuring Access and Support: By providing accurate information, comprehensive counseling, and accessible healthcare services, individuals can make informed decisions about their reproductive health and receive the support they need throughout the Medical Abortion process.
Future Directions: Continued research and advocacy efforts are essential to expand access to Medical Abortion, improve treatment protocols, and ensure the safety and well-being of individuals seeking reproductive healthcare services. Through ongoing innovation and collaboration, Misoprostol remains a cornerstone in the realm of Medical Abortion, empowering individuals to exercise their reproductive rights and make choices that align with their values and preferences.
5. Labor Induction: The Role of Misoprostol
Labor induction is a standard obstetric procedure used to initiate or augment labor when natural labor onset is delayed or when there are medical indications for delivery. Misoprostol, a prostaglandin E1 analog, has emerged as a valuable agent for labor induction due to its effectiveness, ease of administration, and cost-effectiveness. This subsection provides a comprehensive overview of the use of Misoprostol in labor induction, including its mechanisms of action, dosing regimens, safety considerations, and clinical outcomes.
5.1. Understanding Labor Induction
Purpose: Labor induction is performed to initiate uterine contractions and cervical ripening, leading to the onset of labor and eventual delivery of the fetus.
Indications: Labor induction may be indicated in cases of post-term pregnancy, premature rupture of membranes, fetal growth restriction, preeclampsia, or maternal medical conditions that necessitate expedited delivery.
5.2. Mechanisms of Action of Misoprostol
Uterine Contractility: Misoprostol stimulates uterine contractions by binding prostaglandin receptors in the uterine muscle, increasing myometrial activity.
Cervical Ripening: Besides promoting uterine contractions, this substance softens and dilates the cervix, facilitating the passage of the fetus through the birth canal.
5.3. Dosing Regimens
Dosage: The dosage of Misoprostol for labor induction varies depending on factors such as gestational age, cervical ripeness, and maternal characteristics. Standard dosages range from 25 to 50 mcg, administered vaginally every 4 to 6 hours.
Titration: Healthcare providers may titrate the dosage of Misoprostol based on individual patient response, aiming to achieve effective uterine contractions while minimizing the risk of uterine hyperstimulation.
5.4. Administration Protocols
Vaginal Administration: Misoprostol is typically administered vaginally, as this route offers higher bioavailability and faster onset of action compared to oral administration.
Frequency: Misoprostol may be administered every 4 to 6 hours until adequate uterine contractions are achieved or until cervical ripening is sufficient for labor to progress.
5.5. Safety Considerations
Uterine Hyperstimulation: One of the primary concerns with Misoprostol use in labor induction is the risk of uterine hyperstimulation, which can lead to fetal distress and other complications. Close fetal monitoring is essential to detect signs of distress promptly.
Maternal Side Effects: Common side effects of Misoprostol in labor induction may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and fever. These side effects are usually transient and self-limiting.
5.6. Clinical Outcomes
Efficacy: Clinical studies have demonstrated high efficacy rates for labor induction with Misoprostol, particularly in cases of unfavorable cervical conditions or post-term pregnancies.
Maternal and Fetal Outcomes: Labor induction with Misoprostol is associated with favorable maternal and fetal outcomes, including successful vaginal deliveries and low rates of cesarean section.
5.7. Conclusion
A Valuable Tool in Obstetrics: Misoprostol plays a crucial role in labor induction, offering healthcare providers a safe and effective option for initiating labor and facilitating vaginal delivery.
Balancing Efficacy and Safety: While the medicine is associated with high efficacy rates, careful monitoring and dose titration are essential to minimize the risk of uterine hyperstimulation and ensure optimal maternal and fetal outcomes.
Future Directions: Ongoing research and clinical trials are needed to refine dosing regimens, optimize safety protocols, and explore using Misoprostol in specific patient populations, ultimately enhancing the quality of care for women undergoing labor induction.
6. Misoprostol: A Lifesaving Intervention for Postpartum Hemorrhage
Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) remains one of the leading causes of maternal mortality worldwide, posing a significant challenge in obstetric care. Misoprostol, a prostaglandin E1 analog, has emerged as a valuable tool in the prevention and management of PPH, offering a safe, effective, and accessible option for reducing maternal morbidity and mortality. This subsection provides an in-depth exploration of the use of Misoprostol in PPH, encompassing its mechanisms of action, administration protocols, efficacy, safety considerations, and implications for maternal health.
6.1. Understanding Postpartum Hemorrhage
The magnitude of the Problem: Postpartum hemorrhage, defined as blood loss of 500 ml or more within 24 hours of childbirth, accounts for a significant proportion of maternal deaths globally, particularly in low-resource settings.
Causes: PPH can occur due to uterine atony, retained placental tissue, genital tract trauma, or coagulopathies, among other factors. Prompt intervention is crucial to prevent adverse outcomes.
6.2. Mechanisms of Action of Misoprostol
Uterine Contractility: Misoprostol stimulates uterine contractions by binding to prostaglandin receptors in the uterine muscle, promoting uterine tone and reducing postpartum blood loss.
Additional Effects: Besides its uterotonic properties, Misoprostol may help control bleeding by enhancing uterine involution and promoting clot formation.
6.3. Administration Protocols
Prophylactic Use: To prevent PPH, Misoprostol can be administered prophylactically immediately following childbirth. The recommended dosage is typically 600 to 1000 mcg administered orally or sublingually.
Treatment of Established PPH: In cases of established PPH, Misoprostol can be used as a first-line or adjunctive therapy. The dosage and route of administration may vary depending on the severity of bleeding and clinical response.
6.4. Efficacy and Clinical Outcomes
High Efficacy: Clinical studies have demonstrated the high efficacy of Misoprostol in preventing and treating PPH, with significant reductions in blood loss and the need for additional interventions such as uterotonic agents or surgical interventions.
Maternal Outcomes: The timely administration of this medicine in PPH management is associated with improved maternal outcomes, including reduced rates of severe blood loss, transfusion requirements, and maternal morbidity and mortality.
6.5. Safety Considerations
Maternal Side Effects: Common side effects of Misoprostol administration may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and fever. These side effects are generally mild to moderate and transient.
Uterine Hyperstimulation: While uterine hyperstimulation is a potential concern with Misoprostol use, particularly at higher dosages, close monitoring and dose adjustment can help mitigate this risk.
6.6. Accessibility and Implementation Challenges
Global Access: Misoprostol offers a valuable option for PPH prevention and management, particularly in resource-limited settings where access to conventional uterotonic agents such as oxytocin may be limited.
Challenges: Despite its effectiveness, challenges related to drug availability, dosage standardization, and healthcare provider training may hinder the widespread implementation of Misoprostol for PPH management.
6.7. Conclusion
A Vital Tool in Obstetric Care: Misoprostol represents a vital tool in the prevention and management of postpartum hemorrhage, offering a safe, effective, and accessible option for reducing maternal morbidity and mortality worldwide.
Future Directions: Continued efforts are needed to address implementation barriers, expand access to Misoprostol, and further refine its use in PPH management through research, education, and advocacy initiatives. Through collaborative efforts, Misoprostol has the potential to significantly improve maternal health outcomes and contribute to global efforts to reduce maternal mortality.
7. Navigating Gastric Ulcers: The Therapeutic Role of Misoprostol
Gastric ulcers, a common gastrointestinal disorder, can cause significant discomfort and complications if left untreated. Misoprostol, a synthetic prostaglandin E1 analog, has emerged as an effective therapeutic option for the prevention and treatment of gastric ulcers, particularly those induced by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). This subsection aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the use of Misoprostol in gastric ulcers, exploring its mechanisms of action, dosing regimens, efficacy, safety considerations, and clinical implications.
7.1. Understanding Gastric Ulcers
Nature of Gastric Ulcers: Gastric ulcers are erosions or breaks in the mucosal lining of the stomach, often caused by factors such as Helicobacter pylori infection, NSAID use, excessive alcohol consumption, or stress.
Clinical Presentation: Symptoms of gastric ulcers may include abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, and gastrointestinal bleeding. Complications such as perforation or bleeding can occur in severe cases.
7.2. Mechanisms of Action of Misoprostol
Gastric Mucosal Protection: Misoprostol exerts its therapeutic effects by enhancing gastric mucosal protection through several mechanisms, including increasing mucosal blood flow, promoting mucus secretion, and inhibiting gastric acid secretion.
NSAID-Induced Gastric Damage: Misoprostol is particularly effective in preventing NSAID-induced gastric damage by counteracting the harmful effects of NSAIDs on gastric mucosa and reducing the risk of ulcer formation.
7.3. Dosing Regimens
Dosage: Misoprostol’s dosage for gastric ulcer prevention typically ranges from 200 to 400 mcg, administered orally four times daily with meals and at bedtime. The dosage may vary depending on the severity of the ulcer and individual patient response.
Duration of Treatment: The duration of Misoprostol treatment for gastric ulcers may vary, but it is often continued for numerous weeks to promote ulcer healing and reduce the risk of recurrence.
7.4. Clinical Efficacy and Outcomes
Prevention of NSAID-Induced Ulcers: Clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of Misoprostol in preventing NSAID-induced gastric ulcers, with significant reductions in the incidence of ulcers and gastrointestinal complications in high-risk patients.
Treatment of Existing Ulcers: Misoprostol also promotes the healing of existing gastric ulcers, mainly when combined with other ulcer-healing therapies such as proton pump inhibitors or antibiotics for H. pylori eradication.
7.5. Safety Considerations
Gastrointestinal Side Effects: Common gastrointestinal side effects of Misoprostol may include diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and nausea. These side effects are usually mild to moderate and resolve with continued use.
Uterine Effects: Misoprostol carries a potential risk of uterine contractions and miscarriage, making it contraindicated in pregnant individuals or those at risk of pregnancy.
7.6. Accessibility and Implementation Challenges
Global Access: Misoprostol is widely available and affordable. It is an attractive option for gastric ulcer prevention and treatment, particularly in low-resource settings where access to other ulcer therapies may be limited.
Adherence and Compliance: Challenges related to dosing frequency and gastrointestinal side effects may affect patient adherence to Misoprostol therapy, highlighting the importance of patient education and support.
7.7. Conclusion
A Cornerstone in Ulcer Management: Misoprostol plays a crucial role in the prevention and treatment of gastric ulcers, offering a safe, effective, and accessible option for patients at risk of NSAID-induced ulceration or those with existing ulcers.
Future Directions: Continued research and innovation are needed to optimize Misoprostol therapy further, address implementation challenges, and improve outcomes for patients with gastric ulcers. Through collaborative efforts, Misoprostol has the potential to continue making a significant impact in the management of gastric ulcer disease globally.
8. Conclusion
Versatile and Valuable: Misoprostol is a versatile and valuable medication with wide-ranging applications across various medical specialties. Its diverse mechanisms of action and well-established safety profile make it a cornerstone in modern healthcare, offering safe and practical solutions to numerous medical challenges.
Through ongoing research, innovation, and responsible use, Misoprostol continues to shape the landscape of contemporary medicine, improving outcomes and enhancing patient care.
9. Reference:
Misoprostol: Uses, Dosage, Side Effects & Warnings
Author
 Dr. Kopp Kallner. M.D. in Obstetrics & Gynecology, Columbia University Medical School.
Dr. Kopp Kallner. M.D. in Obstetrics & Gynecology, Columbia University Medical School.
Buy Abortion Pills
Our products
Abortion Pill
Buy Abortion Pill online the UK or Europe, and the US
Abortion Pill contains 5 tablets: 1 Mifepristone tablet by 200 mg with 4 Misoprostol tablets by 200 mcg. It's convenient till 11 gestational weeks.
AntiPREG Kit
Buy Abortion Pills online in the US, Europe, Worldwide
AntiPREG Kit includes Mifepristone 200mg and Misoprostol 800mcg.
This should take up to 77 days or 11 pregnancy weeks
Abortion Pill Kit
Buy Abortion Pill Kit online in the US, Europe, and Worldwide
Abortion Pill Kit contains 5 tablets: 1 Mifepristone tablet by 200mg with 4 Misoprostol tablets by 200mcg. It's convenient till 11 gestational weeks
Cytolog
Buy Cytolog online in the US, Europe, and Worldwide
Cytolog contains 8 tablets: 2*4 Misoprostol tablets by 200mcg
Cytotec
Buy Cytotec online in the US, Europe, and Worldwide
Cytotec contains 8 tablets: 2*4 Misoprostol tablets by 200mcg
Generic RU-486
Buy Generic RU-486 online in the US, Europe, Worldwide
Generic RU-486 contains 10 tablets: 10 Mifepristone tablets by 25mg. Total 250mg
Medabon
Buy Medabon online in the US, Europe, Worldwide
Medabon contains 5 tablets: 1 Mifepristone tablet by 200mg with 4 Misoprostol tablets by 200mcg. It's convenient till 11 gestational weeks
Mifegymiso
Buy Mifegymiso online in the US, Europe, and Worldwide
Mifegymiso contains 5 tablets: 1 Mifepristone tablet by 200 mg with 4 Misoprostol tablets by 200mcg. It's convenient till 11 gestational weeks.
Mifegyne
Buy Mifegyne online in the US, Europe, and Worldwide
Mifegyne contains 10 tablets: 10 Mifepristone tablets by 25 mg. Total 250 mg.
 Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Русский
Русский