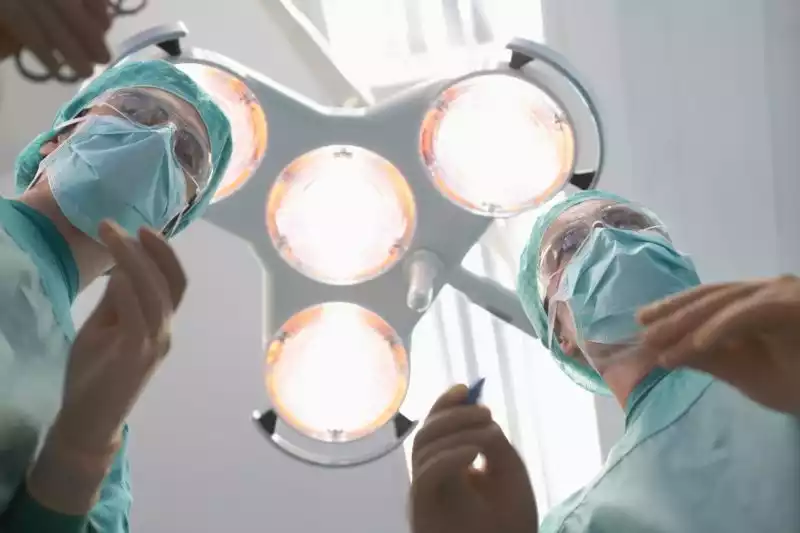
Medical vs. Surgical Abortion: Understanding the Differences
November 26, 2023 15:09
February 24, 2025 5:57
Introduction:
When faced with an unplanned pregnancy, individuals may consider different options available to them, including abortion. Two standard methods for terminating a pregnancy are medical abortion and surgical abortion. Understanding the differences between these two procedures is essential to make an informed decision.
This article aims to provide an overview of medical vs. surgical termination of pregnancy, outlining their processes, effectiveness, and potential risks.
Medical Abortion:
Medical abortion, also known as medication or non-surgical abortion, involves the use of specific drugs to terminate a pregnancy. It is typically performed in the early stages of pregnancy, up to 11 weeks gestation. Abortion in the first abortion.
The Process:
Medical abortion involves two medications, Mifepristone and Misoprostol. The process typically includes the following steps:
- Administration of Mifepristone: This medication blocks the hormone progesterone necessary for maintaining pregnancy.
- Administration of Misoprostol: Usually taken 24 to 48 hours after mifepristone, misoprostol causes the uterus to contract and expel the pregnancy.
Effectiveness:
Medical abortion is highly effective, with success rates of up to 95-98% when performed within the recommended timeframe. However, there is a small risk of incomplete abortion, which may require further medical intervention.
Risks and Side Effects:
Common side effects of medical abortion may include heavy bleeding, cramping, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue. While severe complications are rare, it is crucial to be aware of potential risks, such as infection, allergic reactions, and failure to terminate the pregnancy.
Surgical Abortion:
Surgical abortion involves a surgical procedure to remove the pregnancy from the uterus. This method is typically performed in the first or second trimester of pregnancy.
Types of Surgical Abortion:
- a. Manual Vacuum Aspiration (MVA): This is a standard method used in the first trimester, in which suction is used to remove the pregnancy.
- b. Dilation and Curettage (D&C): D&C involves dilating the cervix and using a curette or suction to remove the pregnancy.
- c. Dilation and Evacuation (D&E): D&E is performed in the second trimester and involves dilating the cervix and removing the pregnancy using suction and surgical instruments.
Effectiveness:
Surgical abortion is generally considered highly effective, with success rates exceeding 99% for early gestation procedures. The effectiveness may vary slightly depending on the specific technique used and the gestational age of the pregnancy. To calculate your gestational age.
Risks and Side Effects:
Surgical abortion carries some risks, including infection, bleeding, injury to the uterus or cervix, and potential complications associated with anesthesia. However, serious complications are rare, mainly when a skilled healthcare professional performs the procedure.
Emotional Considerations:
Both medical abortion and surgical abortion can have an emotional impact on individuals. Some people may experience feelings of relief, while others may struggle with complex emotions, such as grief or guilt. It is essential to acknowledge and prepare for the potential emotional aftermath. Counseling or support groups can benefit those dealing with emotional challenges.
Accessibility and Availability:
The availability of medical and surgical abortion can vary depending on the region and the prevailing legal and social norms. Medical abortion can generally be administered in clinics or through telemedicine, allowing for greater accessibility, particularly in areas where surgical abortion may be less accessible or prohibited. Understanding the local laws and regulations is crucial when considering these options.
Personal Preferences and Health Considerations:
Individual preferences, potential medical conditions, and gestational age can influence the choice between medical or surgical abortion. Some may prefer the privacy and control that medical abortion offers, while others may opt for a surgical procedure for personal reasons or if they are further along in their pregnancy.
Follow-up Care:
After both medical and surgical abortion, it is essential to have access to follow-up care. This may include a physical examination to ensure the successful completion of the procedure, assess any potential complications, and address concerns or questions. It is crucial to discuss post-abortion care and contraception options with a healthcare professional during the decision-making process.
Conclusion:
Choosing between medical abortion and surgical abortion is a deeply personal decision that should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional. Understanding the differences in process, effectiveness, risks, and emotional considerations can help individuals make informed choices that align with their specific circumstances and preferences.
Remember to consult a healthcare professional, as they can provide personalized guidance tailored to your unique needs.
 Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Русский
Русский