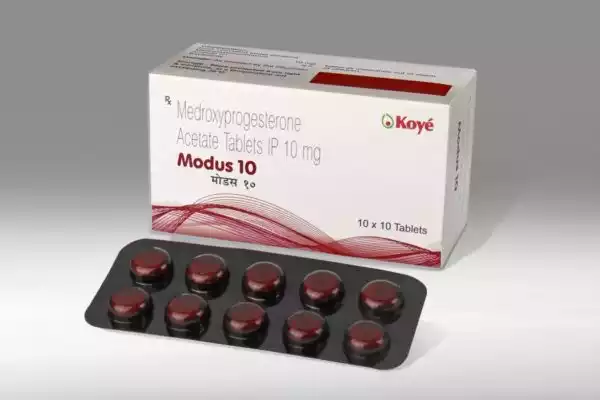
Product description
What Is The Modus Tablet?
Additionally, the secretory or moist endometrium sheds rapidly in the absence of pregnancy. Progestins have been synthesized artificially since the 1950s; they have witnessed several advancements throughout generations, and the fourth generation is presently in use.
One such synthetic progestin is Medroxyprogesterone. Although a first-generation type, Modus has practical applications in various women’s health issues, ranging from dysfunctional uterine bleeding to cancer hormone therapy.
Additionally, we provide Depot Provera Contraceptive Injection, including the active ingredient Medroxyprogesterone Acetate (MPA). This medication is used for contraception and other purposes.
Marketing and Active Ingredients for Modus 10mg Tablets
Modus 10mg tablets are manufactured by GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals and contain the formulated salt of the first-generation progestin Medroxyprogesterone.
Modus Tablets: Ingredients and Formulation
Modus is a prescription medication with the active ingredient medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA). Modus pills are available in blister packs with ten tablets in either 2.5mg or 10mg.
Manufacturer of Modus Tablets. GlaxoSmithKline is a pharmaceutical business. www.gsk.com
How do Modus tablets work? – Pharmacodynamics and Modus Operandi
Although progestins are most often used with the oral contraceptive pill, Medroxyprogesterone is not generally available in its oral form owing to the desire for more potent and newer progestin agents. Progesterone is involved in a range of female genital system processes. It increases mammary gland development to prepare the breast for lactation.
Cervical secretions, previously watery, become viscid and resistant to sperm entry into the cervix. Tablets containing synthetic progestins have a secondary contraceptive action.
Progesterone, especially in the uterus, alters the secretory function of an estrogen-treated endometrium by increasing blood flow, gland tortuosity, and secretions.
Menstruation occurs due to progesterone shortage due to the loss of this secretory endometrium (womb lining). Similarly, artificial menstruation, also called “withdrawal bleeding,” occurs when an exogenous progestin suction period of five to fifteen days is withdrawn.
Prolonged exposure to continuous progesterone and long-term injectable formulations of Medroxyprogesterone causes the uterine lining to become soggy or spongy (decidualized), which is highly contraceptive.
LH and FSH are two brain-derived hormones tightly controlled by ovarian estrogen/progestin in a coordinated hormonal feedback loop. Medroxyprogesterone is a tablet or injection that significantly reduces LH/FSH levels, limiting ovarian estrogen production.
This effect becomes more pronounced with time, eventually reaching menopausal symptoms when endogenous estrogen is eliminated. This condition is crucial for preventing and treating estrogen-dependent cancers such as breast, uterine, and kidney tumors.
Indications and Modalities for Modus Dosage
Modus dose is defined or adjusted based on the clinical situation in which it is utilized. For example, dosages ranging from 2.5 to 5 or even 10 mg per day are used in single or divided doses to treat dysfunctional uterine bleeding in the latter half of the menstrual cycle.
2.5 mg daily is used at the end of the HRT or Hormone Replacement Therapy cycle.
Greater doses are utilized in cancer prevention and palliative treatment, ranging from 300 mg to 1.5 grams daily, depending on the tissue. Other businesses, like Deviry, provide formulations with a greater strength of 100mg each tab.
Modus Tablets: Clinical Applications, Usages, and Indications of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding:
Modus is used in the second part of the ovulatory cycle. This phase is called the luteal phase, and many women have low progesterone levels at this time, which results in irregular menstrual cycles or flow. Between days 16 and 25, this supplement aids in the healing of irregular cycles.
Menorrhagia or abnormally heavy periods also benefit from this treatment, especially when administered cyclically over three to six months. In addition, due to the presence of estrogens throughout the early portion of the menstrual cycle, the medicine is more successful at reducing menstrual pain and flow volume, hence treating dysmenorrhea and iron deficiency anemia (from excessive blood loss).
Secondary: Amenorrhoea
Amenorrhoea is defined as the absence of menstruation for six months or more in a woman who has previously menstruated regularly and is not nearing menopause. Numerous causes may contribute to the development of this condition, including stress, rexia, extreme exercise, and thyroid or pituitary abnormalities. While identifying the cause is vital, Modus is critical in reintroducing menstruation to these women through a withdrawal bleed.
Replacement Therapy with Hormones (RTH)
Modus must be used in the second half of the cycle in combination with low-dose estrogens in the first half of the process in women with an intact uterus undergoing hormone replacement therapy.
Modus protects the endometrium of the uterus from excessive and unopposed stimulation, hence preventing malignant changes.
PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome):
This is a relatively common ailment in the current day. It presents itself in various ways, the most prominent being anovulation, oligomenorrhoea, and infertility. Women with Polycystic Ovaries benefit from cycle resets and testosterone suppression. Modus supports these women in resuming their periods and prevents the uterine lining from thickening uncontrollably.
Endometriosis:
This is a condition caused by ectopic endometrium growing outside the uterus. It is mainly characterized by menstruation pain (dysmenorrhea) and infertility concerns.
Continuous administration of Modus/Progestins may result in near-total menopause or experimentally caused gonadal atrophy, indirectly inhibiting endogenous estrogen production by decreasing central gonadotropins (LH/FSH). Modus is a treatment option for endometriosis.
Endometrial Hyperplasia:
Modus is an efficient medical treatment procedure for simple endometrial hyperplasia, a premalignant lesion of the womb lining or endometrium. Modus, whether provided daily at a dosage of 10 to 20 mg or cyclically 12 to 14 days per month, has been shown to assist numerous women in overcoming this condition. On the other hand, Mirena and Megestrol are recommended in situations of complex or atypical hyperplasia.
Cancer Treatment:
Modus is combined with hormone treatment to treat PR + ve breast cancer (progesterone receptor expressing). In addition, MPA may be used to treat advanced endometrial, prostate, and kidney cancers on a palliative basis, although at substantially higher doses.
Adverse Reactions to Modus Tablets
Modus tablets may produce temporary, mild side effects. The side effects of Medroxyprogesterone vary according to the dose and type used.
Modus is associated with a higher incidence of adverse effects when provided in 2.5 or 10mg doses for short periods to treat dysfunctional uterine bleeding or secondary amenorrhoea than Depot Provera or higher doses used in cancer treatment regimens.
- During therapy, intermittent spotting is referred to as “breakthrough bleeding.”
- With prolonged usage, there is a risk of temporary infertility;
- Acne vulgaris, hirsutism, and alopecia are three common skin conditions;
- Dermatitis, urticaria;
- Nausea, Vomiting, and Diarrhea;
- Aches and spasms in the muscles;
- Breast enlargement/fullness, pelvic infections, and cervical erosions;
- Possible complications include palpitations, hypertension, thrombosis, myocardial infarction, and stroke.
Adverse Reactions and Disadvantages of Modus Tablets
Teratogenicity is seen in women who take Modus while unaware of or uneducated about pregnancy by webbed toes and fingers, masculinization of female newborn genitalia, and low birth weight children.
Modus, like other progestins, increases fluid retention and fat accumulation. Therefore, weight gain is mainly proportional to the duration of therapy.
Increased glucose intolerance and hyperglycemia are extensively recognized.
Breast cancer may be utilized for a prolonged period beyond two years, primarily by younger women aged 25-35.
Interactions & Interference with Modus Treatment
The following medicines are effective at impairing Modus’s efficacy:
Aminoglutethimide, Griseofulvin, Rifampin, Phenobarbital, Phenytoin, and Carbamazepine are all known enzyme inducers that reduce the effectiveness of MPA. Therefore, these medications should be handled with care when used for contraception.
Plasma gonadotropin levels, urine steroid levels, and coagulation profiles may all be affected while taking MPA.
Contraindications And Precautions About Operational Mode
Modus should be avoided in the following situations, and care should be used if medical counsel is sought:
- MPA hypersensitivity or allergy (Medroxyprogesterone Acetate);
- Suspected pregnancy, unexplained vaginal bleeding, menstrual cycle irregularity/uncertain dates;
- Breast lumps of unknown origin, higher risk of breast cancer, and breast cancer diagnosis;
- Among other things, an increased risk of blood coagulation issues, thrombotic events, thromboembolism, stroke, and uncontrolled hypertension;
- Before commencing Modus, patients with preexisting medical conditions such as epilepsy, seizures, or migraine should visit their physician;
- For women with cervical lesions or a high risk of cervical cancer or intraepithelial neoplasia, a Pap smear and/or colposcopy are indicated.
Shipping Restrictions
There are no shipping restrictions on this item.
 Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Русский
Русский