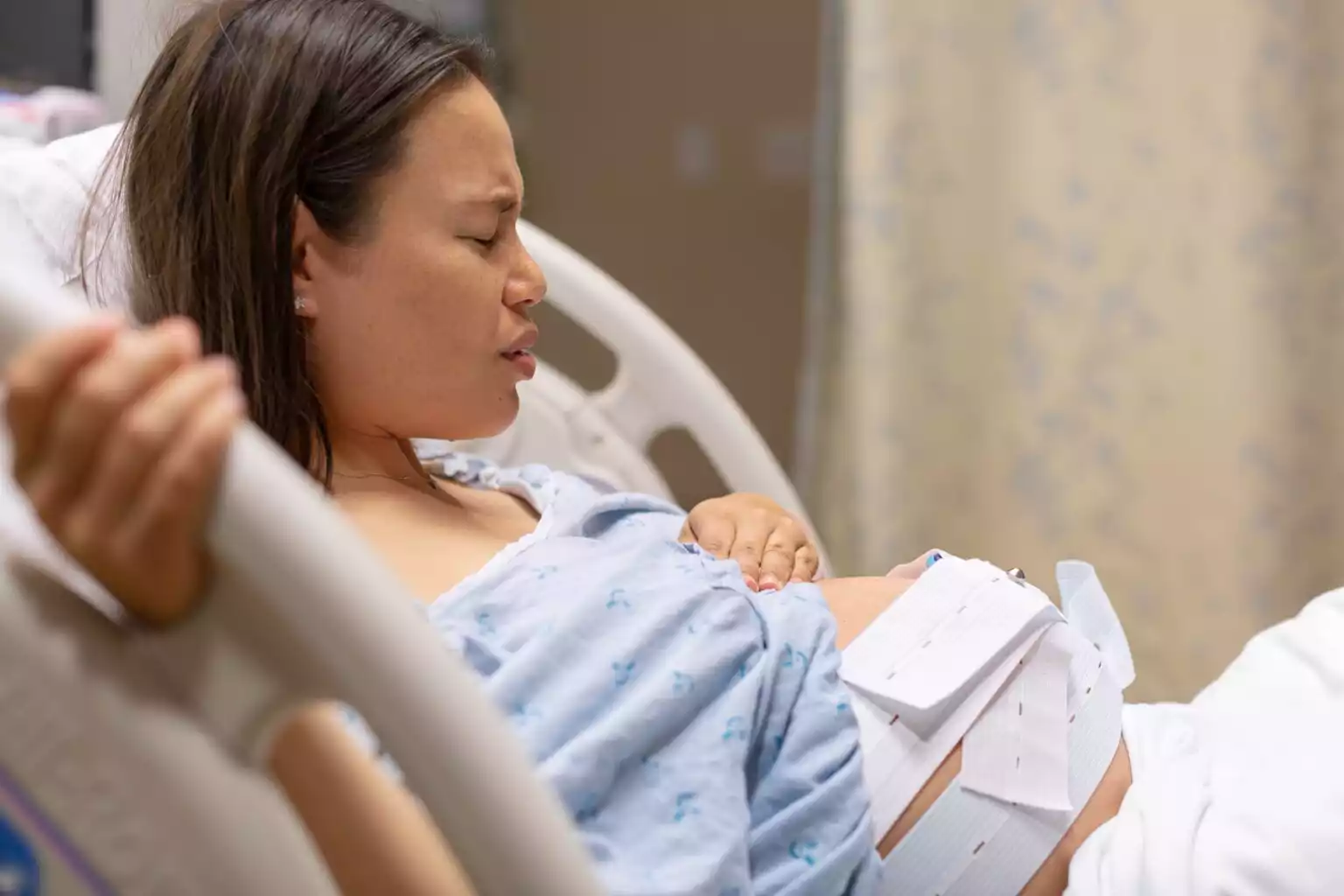

Induced Labor for Pregnancy Termination: A Comprehensive Guide
February 16, 2024 14:28
November 03, 2024 9:12
Introduction:
Induced labor for pregnancy termination, also known as labor induction abortion, is a medical procedure used to terminate a pregnancy. It is essential to understand the historical background, steps of the procedure, indications, contraindications, potential complications, and the legal status of the procedure in the United States and the European Union.
It is a sensitive subject with varying opinions and legal considerations in different jurisdictions. In this article, we will explore the steps involved in the procedure, indications for induced labor, contraindications, and potential complications.
Historical Background:
The history of induced labor for pregnancy termination traces back to ancient times when various methods were used to terminate unwanted pregnancies. Over the years, advancements in medical knowledge and technology have contributed to the development of safer and more effective techniques.
Steps of the Procedure:
Induced labor for pregnancy termination involves several steps. Here is a general overview:
1. Pre-assessment:
Before inducing labor, a healthcare provider will conduct a thorough medical history evaluation and physical examination. They will also perform relevant tests, such as blood tests, ultrasound, and possibly an assessment of the gestational age.
2. Preparing the cervix:
In most cases, the cervix needs to be softened and dilated before the induction of labor. This can be achieved by using medication, such as Misoprostol or Mifepristone, or by mechanical dilation methods.
3. Medication administration:
Once the cervix is prepared, medications such as prostaglandins or synthetic Oxytocin (Pitocin) may be administered. These medications work by stimulating uterine contractions to induce labor.
4. Monitoring and support:
Throughout the induction process, the woman will be closely monitored for any signs of complications. Monitoring can include regular checks of the fetal heart rate, uterine contractions, and vital signs of the woman. Emotional and psychological support is also provided.
5. Expulsion of the fetus:
As uterine contractions become stronger and more regular, the fetus, and then the placenta, are expelled from the uterus. This results in the expulsion of the pregnancy, similar to a natural delivery. The woman may experience strong cramping and bleeding during this phase.
Indications for Induced Labor for Pregnancy Termination:
The procedure for pregnancy termination is typically performed in specific situations where the termination of a pregnancy is deemed necessary. These indications may include:
1. Fetal anomalies: When significant fetal abnormalities are detected, induced labor may be recommended. This allows for the termination of a pregnancy where the fetus is unlikely to survive or experience a reasonable quality of life.
2. Maternal health concerns: If a pregnancy poses a substantial risk to the mother’s physical or mental health, induced labor for pregnancy termination may be considered. This can include severe medical conditions or complications during pregnancy.
3. Unwanted pregnancy: Induced labor may be considered when a woman chooses to terminate a pregnancy voluntarily within the legal framework of her country.
Contraindications:
While induced labor may be a safe procedure for most individuals, there are certain situations where it may not be recommended. Some potential contraindications include:
1. Advanced gestational age: This procedure may have specific gestational limits, and alternate procedures may be recommended after a certain point in pregnancy.
2. Maternal medical conditions: Some medical conditions, such as uncontrolled bleeding disorders or severe heart disease, may make the medical procedure unsafe. In such cases, alternative methods of termination may be considered.
3. Active pelvic infection: If the pregnant individual has an active pelvic infection, the procedure may be postponed until the infection is treated and resolved.
Complications of induced labor:
As with any medical procedure, this procedure for pregnancy termination carries potential risks and complications, including:
1. Heavy bleeding: Induced labor carries a risk of excessive bleeding, which may require further medical intervention.
2. Incomplete abortion: There is a possibility that the procedure may not thoroughly remove pregnancy tissue, requiring additional medical intervention.
3. Infection: Any procedure involving the uterus carries a risk of infection. Symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and foul-smelling discharge.
4. Emotional impact: Pregnancy termination can have emotional implications, and some women may experience feelings of grief, guilt, or regret. Access to counseling services is crucial in providing emotional support.
Legal Status of induced labor in the US and EU:
The legal status of induced labor for pregnancy termination varies across countries, including the United States and the European Union. Laws and regulations governing induced labor differ, and restrictions on the procedure can vary significantly. It is crucial to consult healthcare professionals and understand the legal requirements in your specific jurisdiction.
Conclusion:
Induced labor for pregnancy termination is a medical procedure that requires careful consideration, adherence to legal requirements, and access to appropriate healthcare services. It is vital for women seeking induced labor to consult a healthcare professional who can provide personalized advice and support throughout the process.
The decision to undergo induced labor for pregnancy termination is deeply personal, and each individual’s circumstances need to be considered by qualified medical professionals.
Author
 Dr. Kopp Kallner. M.D. in Obstetrics & Gynecology, Columbia University Medical School.
Dr. Kopp Kallner. M.D. in Obstetrics & Gynecology, Columbia University Medical School.
 Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Русский
Русский