Abortion Pills: Overview
December 07, 2023 17:27
November 03, 2024 9:13
Introduction
Abortion is a sensitive and controversial topic that elicits strong opinions from different individuals and communities. It is important to approach the topic with empathy, respect, and accurate information. In this article, we will provide an overview of abortion pills, also known as medication abortions, including their purpose, process, and significant considerations.
However, it is crucial to bear in mind that this article is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional consultation or medical advice.
What are Abortion Pills?
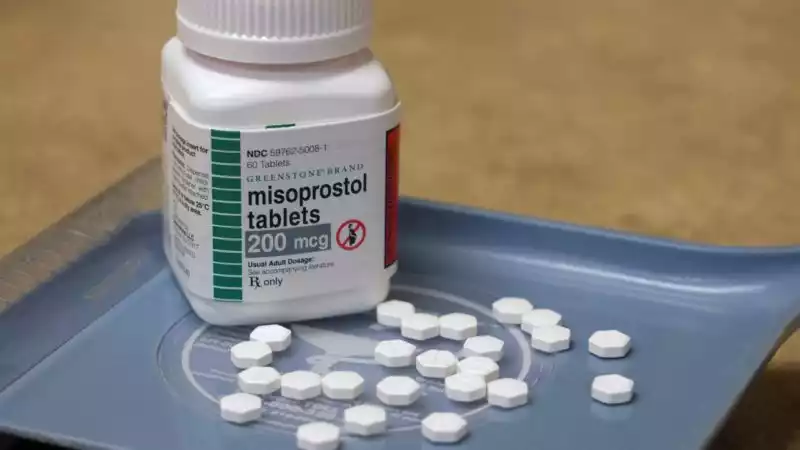
Abortion pills, also known as medication abortions or medical abortions, are a non-invasive and non-surgical method of terminating an early pregnancy (usually up to 10 weeks gestation). This method involves the use of medications, under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare professional, to induce the termination.
There are two primary medications involved in a medical abortion:
- Mifepristone (RU-486): This medication is taken orally and works by blocking the hormone progesterone, which is necessary for maintaining a pregnancy. By blocking progesterone, the lining of the uterus breaks down, and the pregnancy cannot continue.
- Misoprostol: This medication is taken buccally (placed between the cheek and gum), vaginally, or sublingually (under the tongue). Misoprostol causes contractions in the uterus, leading to the expulsion of the pregnancy.
Process of Medical Abortion:
A medical abortion typically consists of multiple steps, which may vary slightly depending on the healthcare provider and country:
- Consultation: Before initiating a medical abortion, it is important to consult a healthcare professional who can assess the viability and duration of the pregnancy. They will also explain the process, potential risks, and provide necessary information.
- Administration of Mifepristone: The first medication, Mifepristone, is usually taken orally in the presence of a healthcare professional. This medication blocks progesterone and prepares the body for the expulsion of the pregnancy.
- Follow-up Visits: After taking Mifepristone, follow-up visits may be required to monitor the progress of the abortion and provide any necessary support or additional medications.
- Administration of Misoprostol: Typically, 24 to 48 hours after taking Mifepristone, the second medication, Misoprostol, is administered. The method of administration (buccal, vaginal, or sublingual) may vary depending on the healthcare provider’s recommendation.
- Expulsion of the Pregnancy: Following the administration of Misoprostol, contractions in the uterus will occur, resulting in the expulsion of the pregnancy. This can happen within a few hours or take as long as several days.
- Follow-up Care: After the abortion is completed, it is important to schedule a follow-up visit with a healthcare professional. This visit allows them to ensure the procedure was successful and address any concerns or complications.
Important Considerations:
While medical abortions are considered safe and effective, there are important considerations and potential risks:
- Efficacy: Medical abortions have a success rate of approximately 95% to 98%. However, in some cases, the abortion may be incomplete, and surgical intervention may be required.
- Side Effects: Common side effects of medical abortions include cramping, bleeding, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue. These symptoms are usually temporary and resolve on their own.
- Emotional Impact: Termination of pregnancy can lead to a range of emotions and may have a significant psychological impact on individuals. It is essential to have access to emotional support, both during and after the procedure.
- Medical Follow-up: Follow-up visits with a healthcare professional are essential to ensure the complete expulsion of the pregnancy and address any complications.
- Legal and Access Restrictions: The availability and legality of medical abortions vary across countries and regions. It is essential to consider local law.
 Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Русский
Русский